Thyroid is Toxic. What is It?
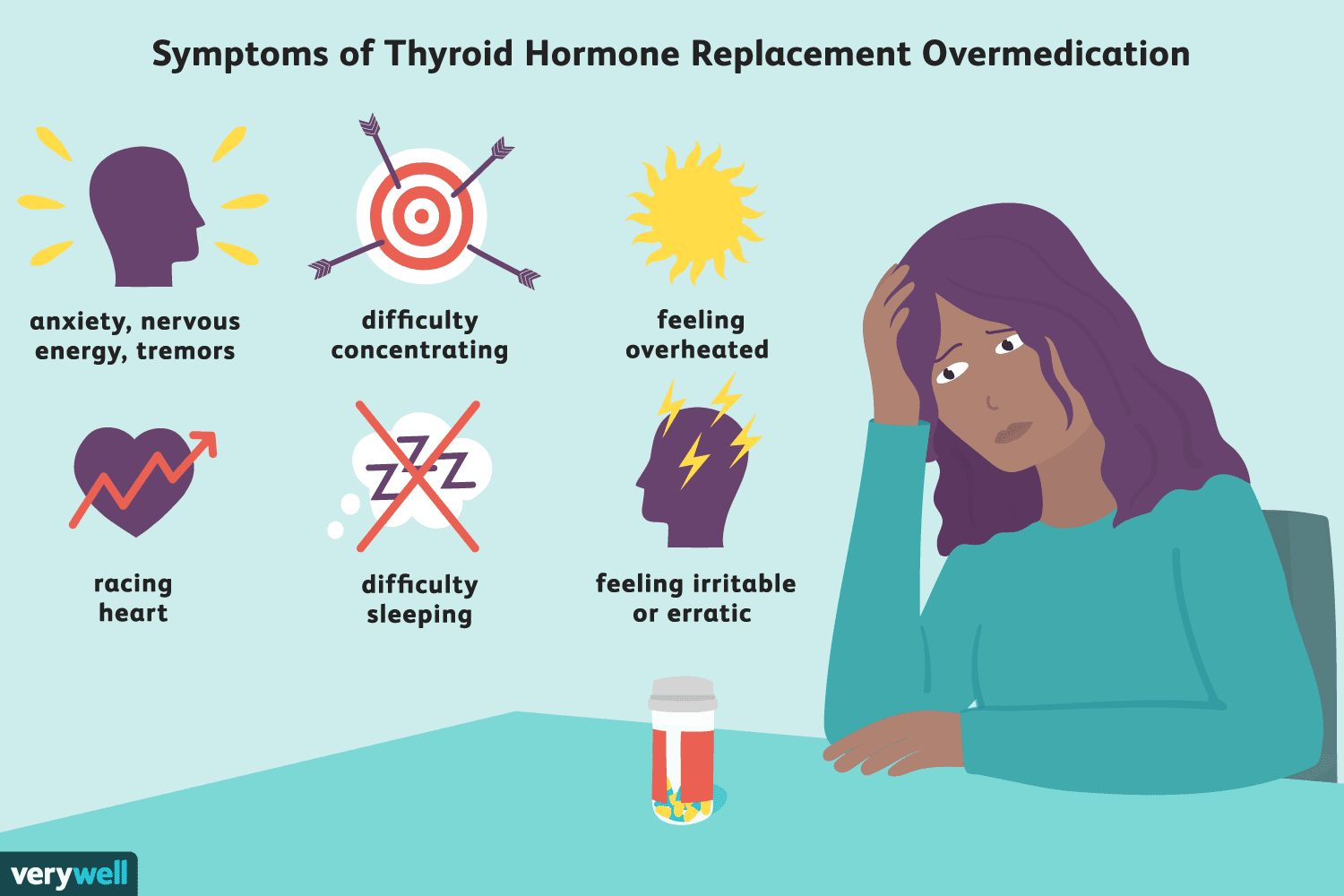
Thyroid is toxic. what is it? Hyperthyroidism is the most common form of this condition. Symptoms of this disease are heart failure, irregular heart beat, and dizziness. In some cases, untreated toxic nodules can lead to osteoporosis, which results in weak bones. Some of the symptoms associated with enlarged thyroid glands include trouble breathing, since the enlargement may press on the windpipe or food pipe.
A non-functioning thyroid gland is common in newborns, and can result in physical and mental problems later in life. Because of this risk, all newborns are given screening blood tests to check thyroid function. In many cases, nodules are the cause of hyperthyroidism. A single nodule causes the condition, known as a toxic autonomous functioning thyroid nodule, while multiple nodules form a multi-nodular goiter.
A non-functioning thyroid gland occurs in one in every 4,000 newborns, and is associated with mental and physical difficulties later in life. The American Thyroid Association recommends that all newborns have a screening blood test to check for a dysfunctional thyroid gland. The overactive thyroid gland is also known as a diffuse toxic goiter. If there are nodules, it results in hyperthyroidism, or hyperthyroidism. Toxic autonomously functioning thyroid nodules are single nodules; a toxic multi-nodular goiter is a cluster of nodules.
Thyroid is toxic. what is it? A nodule containing radionuclides can cause an enlarged thyroid gland. A multinodular goiter is an example of a toxic nodule. It produces an excessive amount of the thyroid hormone without a signal from the body. A toxic thyroid nodule is the most common type of hyperthyroidism, and the symptoms of this condition are dependent on age and gender.
When a nodule affects the thyroid gland, the condition is called hyperthyroidism. In these cases, the thyroid gland secretes too many hormones. The body's metabolism is overactive. The symptoms of this condition can mimic other conditions, such as a nodular tumor or a pulmonary nodule. If a node is present, it is considered a node.
If a nodule causes hyperthyroidism, it is caused by a pituitary nodule in the thyroid gland. When a nodule blocks iodine from entering the bloodstream, it causes the body to overproduce thyroid hormones. The pituitary gland is located in the center of the skull, below the brain. It is responsible for maintaining proper levels of thyroid hormones in the bloodstream.
A nodule in the thyroid gland is a nodule that causes hyperthyroidism. A nodule in the thyroid gland produces too much thyroid hormone without transmitting any signals. A nodule in the thyroid gland that is a nodule. When this happens, the patient develops hypothyroidism and finds it difficult to regulate hormone levels. A nodule can also be a symptom of an autoimmune disease.
A toxic nodule is a nodule in the thyroid that is causing the thyroid to produce too much thyroid hormone. The condition is caused by a toxic nodule. The nodule will cause hyperthyroidism, and will cause an enlarged thyroid gland. It is also known as a multinodular goitre. If you have this disease, it is important to consult a physician.
Thyroiditis is a condition in which the thyroid is overactive. This is caused by excess thyroid hormones in the blood. In some cases, the nodule is a nodule of iodine in the thyroid. In these cases, the thyroid does not produce any hormones. A nodule can also cause pain. In some cases, there is no pain. However, it can be a sign of hyperthyroidism.
The condition is sometimes referred to as thyrotoxicosis. This condition occurs when the thyroid hormone T4 is too high in the body. Thyroid hormone is responsible for regulating the metabolism. Thyroid patients may be irritable or nervous, which means they have a high risk of developing hyperthyroidism. A doctor should look at the nodules in the thyroid and determine if they are cancerous.
